New soil map layers for Field Insights
Field Insights™ continues to improve and impress! Our flagship farmer tool, Field Insights, has added additional soil data map layers and soil components to help your farmers make the best decisions regarding their farm operations. All existing and newly added layers have descriptive popup windows that include a legend (where applicable). Our new map layer dropdown and map components are also categorized for more intuitive searches. Learn more about each new layer and component.
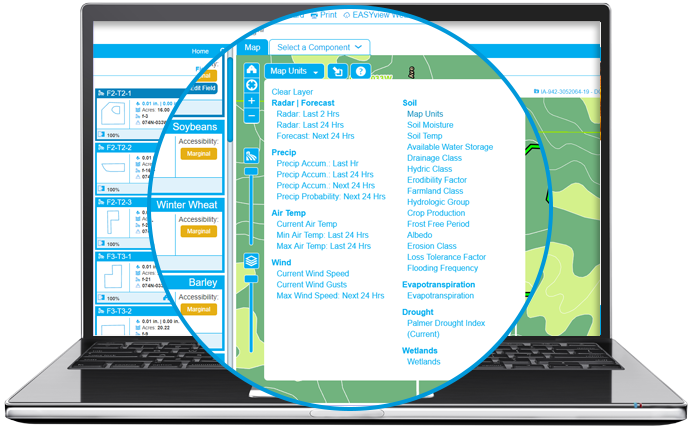
All about the soil map layers
The Map Layers within Field Insights provides crucial weather information at a field level allowing your farmer to see what is taking place on their field without having to leave the house! Each layer provides a different set of information, but all can be similarly read with our user-friendly legend on the bottom of each map when data is selected.
Also, click on the “question mark” icon ![]() to view a popup window with full definitions of each layer. Check out what’s new below in addition to our helpful existing map layers.
to view a popup window with full definitions of each layer. Check out what’s new below in addition to our helpful existing map layers.
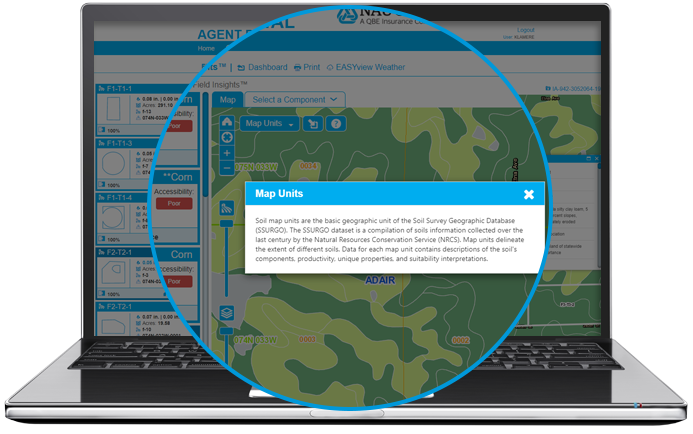
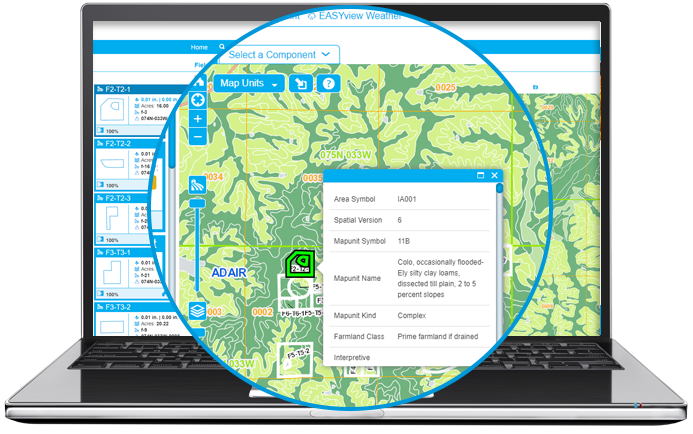
- Interactive Soil Map Units: The basic geographic unit of the Soil Survey Geographic Database (SSURGO) is a compilation of soil information collected over the last century by Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). This layer will delineate the extent of different soils and is utilized for scouting out farmland.
- For Interactivity, click on the
 “Select Fields” icon to select a point (and add a field if you like) and obtain soil information for the underlying soil data. A popup window will appear with the data details.
“Select Fields” icon to select a point (and add a field if you like) and obtain soil information for the underlying soil data. A popup window will appear with the data details.
- For Interactivity, click on the
- Soil Moisture: This legacy layer helps predict field accessibility by looking at the volumetric soil moisture percentage for the 2-5 cm layer based on historical data and current conditions.
- Soil Temp: This legacy layer helps farmers with planning and timing for planting by looking at the soil temp at the 2-5 cm layer based on historical data and current conditions.
- Available Water Storage: The amount of water in soil is based on rainfall amounts, proportion of rain that infiltrates the soil, and the soil’s storage capacity. Utilize this layer for irrigation management since it helps indicate the soil’s ability to retain water.
- Drainage Class: Measures the rate that water drains into the soil, allows farmers to select the type of crop and its field accessibility that would be best for that area’s soil type.
- Hydric Class: Shows where areas, that during the growing season, may have poorly drained soil and will likely flood, pond, or become fully saturated. This layer helps delineate wetland locations.
- Erodibility Factor: Farmers can see if soil in their fields have a high susceptibility to erosion. This can help with field preparation, tillage system management, and understanding about potential soil loss.
- Farmland Class: This layer displays prime, locally important, and unique farmlands for use in implementation of the Farmland Protection Policy Act.
- Hydrologic Group: This layer will help with irrigation management, crop suitability determination by defining the hydrologic soil groups (out of seven different class types) that describe the rate that soil absorbs rainfall. Groups A, B, C, D, and combinations of each where group A’s have the smallest chance for runoff and group D’s exhibit the highest potential.
- Crop Production: Based on the National Commodity Crop Productivity Indexes (NCCPI) rank on capability of soil to produce crops without irrigation. This will be used by farmers to help determine land rent values, and which crop types would be successful when planted.
- Frost Free Period: Farmers can determine the type of crop to plant and when by viewing this layer, which shows the amount of days that normally exist between the last spring and first fall freeze dates.
- Albedo: Measures the reflectivity of an object. Black surfaces reflect little light, where white surfaces are very reflective. This is used to indicate soil absorption and salinity detection.
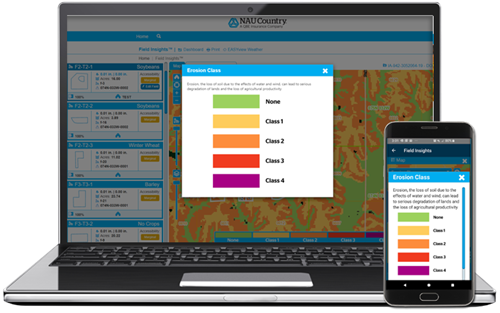
- Erosion Class: This is an additional layer that measures soil erosion potential due to the effects of water and wind and can be used by farmers for field preparation, tillage system management, and understanding potential soil loss.
- Loss Tolerance Factor: Measures the maximum rate of soil loss by tons/acre/year that would still permit crop productivity to be sustained. This helps farmers with tillage system management and soil conservation decisions.
- Flooding Frequency: Farmers can determine which fields would be considered high risk land due to flooding in a given year.
- Actual Evapotranspiration (AE): Manage irrigation by looking at the amount of evapotranspiration that occurs over fields. Water that evaporates returns directly to the atmosphere, while water that is transpired is taken up by plant roots and lost to the atmosphere through the leaves. By combining the two (evapotranspiration (ET)), we can obtain potential crop watering needs.
- Palmer Drought Index: This layer displays the official U.S. Drought Monitor and is updated weekly. This will give a general overview of the state of the growing season, and where dry, moisture starved areas may be impacting farms and ranches. This will assist farmers in managing their risk in Crop Marketing.
- Wetlands: This layer displays wetlands from the National Wetlands Inventory which is produced by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Farmers will be better able to determine land rent values, plan for conservation, and assist in determining in Prevent Plant situations.
Once any of of our Map Layers are selected the map will update showing different color assignments for the applicable data. Simply match the color to the provided legend to further define the data being provided.

NEW! Soil components
Our components also provide valuable data for your farmer’s fields. In order to utilize the components, you or your farmer will first need to select a field by either clicking directly on the field shown in the map, or by clicking the applicable Field Card. Once a field is selected, simply click the “Component” tab and choose the desired component from the categorized drop-down menu. Check out the newly added Soil Component options described below:
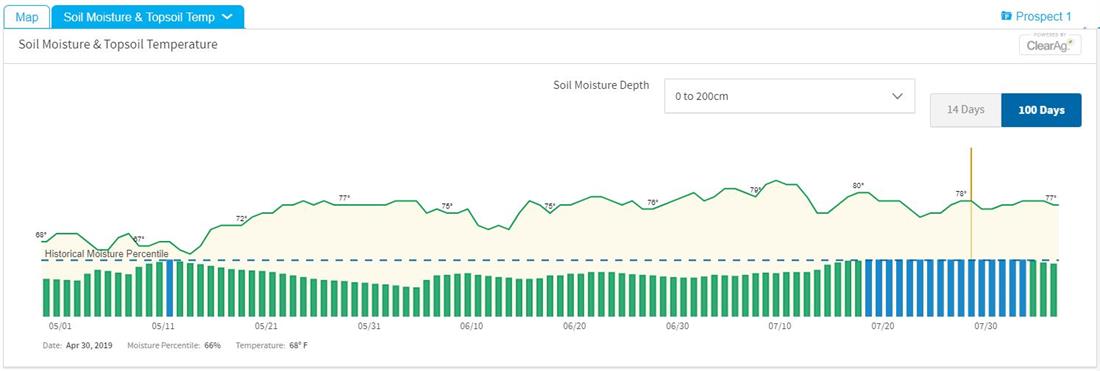
- Soil Moisture & Topsoil Temp: This component will display daily soil temperature and moisture depth percentiles for both 0-10 cm for 0–200 cm for two different displays of time (either 14 days or 100 days). The Soil Moisture component helps predict field accessibility while the Topsoil Temperature will help farmers with planning and timing for planting.
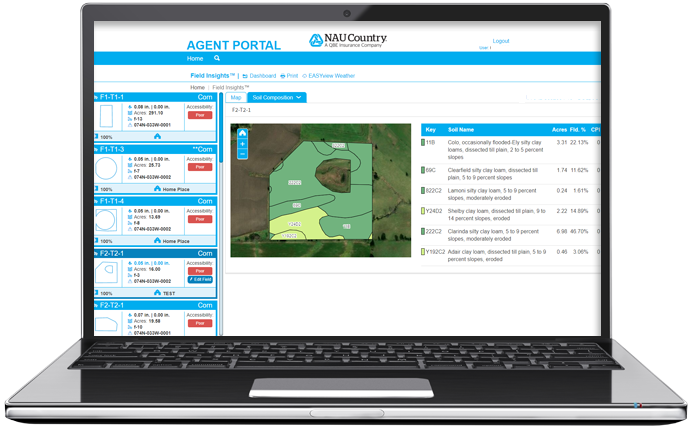
- Soil Composition: Review soil composition details for each field by clicking on the “Field Card” first. The Key will match up the color to the soil composition label within the field. Here, your farmers will see similar data to the Soil Map Unit Layer, which delineates types of soil within a field. This is helpful for variable rate field spraying as well as finding out information of the types of soil on other fields
You already provide the excellent customer service your farmers deserve, now give them more, with Field Insights!
Additional Field Insights resources:
- Weather Metrics
- Field Insights: Harvest Advisor
- Field Insights: Spray Window Advisor
- Mobile Policy Management
- NAU Country Connection Webinar: Field level data at your fingertips with Field Insights!
- Farmer Resources Quick Videos!
How to create a farmer account - Quick Video
How to report acres in Field Insights - Quick Video - Field Insights YouTube Video Tutorials
- NAU Country Expands Iteris ClearAg offerings
